You can query a SQL database using PowerShell’s Invoke-Sqlcmd cmdlet. This cmdlet is included as part of the Sqlps module, which is installed on a computer by running SQL setup. If you need to load the module, use this command:
Import-Module "sqlps" -DisableNameChecking
Note: Including DisableNameChecking suppresses the warning about Encode-Sqlname and Decode-Sqlname.
In this example, we are querying a database with a list of computers and their operating system. You can run most queries this way.
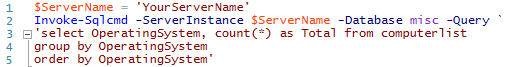
$ServerName = 'YourServerNameGoesHere' #Include \instancename if you are not on the default instance.
Invoke-Sqlcmd -ServerInstance $ServerName -Database misc -Query `
'select OperatingSystem, count(*) as Total from computerlist
group by OperatingSystem
order by OperatingSystem'
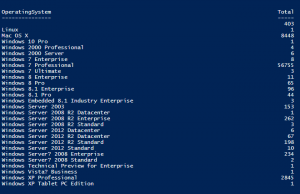
Make sure you put your SQL server’s name in the $ServerName variable, and include the instance name if you are not on the default instance. This screenshot shows the results of the query above on my database.